Our solutions in tax, compliance, and business consulting to help you achieve financial clarity, streamline operations
Reliability analysis for large-scale desalination facility water supply infrastructure serving sustainable development zone spanning 26,500 km²
Critical infrastructure component supporting one of the world's largest integrated sustainable development programs
This Water Intake Pump Station serves as the primary water supply component for a large-scale seawater desalination and treatment system. Located along the coastal shoreline, the facility draws seawater to the downstream desalination plant, which will ultimately deliver up to 500,000 m³/day of treated water to support a sustainable economic zone incorporating industrial cities, ports, research hubs, tourism facilities, residential, and smart infrastructure—all built around innovation and environmental stewardship.
Systematic probabilistic approach evaluating design alternatives and operational scenarios
Developed detailed reliability models capturing N+1 and 2N pump configurations with various standby strategies (hot standby, cold standby, load sharing). Models accounted for common cause failures, maintenance unavailability, and demand-based operational profiles to accurately represent system behavior under normal and degraded conditions.
Executed 500+ Monte Carlo iterations simulating pump failures, maintenance events, and repair activities over a 20-year operational horizon. The simulation incorporated time-varying demand profiles, seasonal variations, and planned maintenance shutdown windows to capture realistic operational scenarios and quantify availability with statistical confidence.
Characterized pump failure mechanisms using Weibull reliability functions fitted to centrifugal pump operating data from similar marine environments. Key failure modes analyzed included mechanical seal failures, bearing degradation, impeller erosion, and motor failures—each modeled with appropriate failure distributions reflecting wear-out, random, and infant mortality characteristics.
Simulated pump station performance under variable demand conditions ranging from initial "First Water" production (30,000 m³/day) to full design capacity (500,000 m³/day). Models captured load-dependent failure rates, turndown constraints, and pump cycling impacts to ensure operability across the full operational envelope.
Redundant pumping system with hot standby configuration ensuring uninterrupted water supply
Configuration: 4 × 25% Duty Pumps + 2 × 25% Hot Standby
Redundancy Philosophy: N+2 with automatic switchover on failure detection
Capacity: Each pump rated for 250,000 m³/day
Availability Requirement: >99% operational availability
Comprehensive evaluation of alternative configurations balancing reliability, cost, and operational flexibility
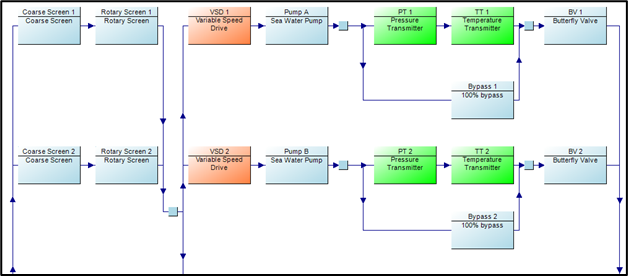
Configuration: 4 Pumps are running + 2 Pumps are standby with Double Forebay
Predicted Availability: 99.9%
✓ Meets 99% availability requirement
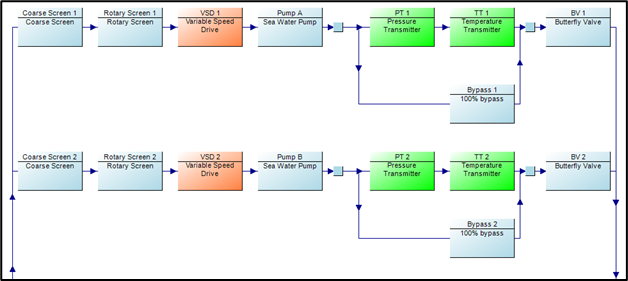
Configuration: 4 Pumps are running + 2 Pumps are standby with Single Forebay
Predicted Availability: 99.9%
✓ Meets all reliability and operational requirements
✓ Provides operational flexibility for ramp-up phase
99.9% Operational Availability
Design Option B selected - exceeds 99% target with robust operational margin
Comprehensive technical documentation supporting design selection and lifecycle planning
Content: Executive summary, design option comparison, availability predictions with confidence intervals, sensitivity analysis, and operational recommendations
Format: Professional PDF (100-150 pages)
Content: Detailed RBD models for each design option showing redundancy logic, failure propagation paths, and operational states
Format: Technical drawings and simulation model files
Content: Lifecycle cost comparison (CAPEX vs OPEX trade-offs), business case justification for recommended option, and ROI quantification
Format: Excel-based financial model
Content: Preventive maintenance schedules, inspection protocols, condition monitoring recommendations, and spare parts requirements
Format: Maintenance planning database
Content: Start-up sequences, normal operations, pump switchover procedures, and emergency shutdown protocols
Format: Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Content: KPI definitions, data collection requirements, performance thresholds, and continuous improvement framework
Format: Operational readiness dashboard specifications
Validated infrastructure reliability ensures consistent water delivery supporting sustainable development and population growth across the economic zone
Optimized pump configuration reduces energy consumption and environmental footprint while maintaining performance requirements
RAM study integrated with digital twin framework enabling predictive maintenance and real-time performance optimization
Infrastructure supports research facilities, technology development, and industrial innovation across the broader economic zone
RAM analysis improves and validate the reliability of brine-handling and energy-intensive systems, ensuring stable ZLD operation with minimal downtime. This reduces energy losses, enhances efficiency, and directly supports the desalination plant’s sustainability and net-zero goals.
Lifecycle optimization approach supports resource efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable operational practices
Validated that recommended design configuration achieves 99.9% operational availability exceeding the 99% target with comfortable operational margin.
Data-driven design selection eliminated unnecessary support structure while maintaining reliability, achieving millions in capital cost savings compared to over-engineered alternatives.
Quantitative comparison of design alternatives provided objective basis for investment decisions with clear cost-benefit justification
Selected configuration supports flexible operations during production ramp-up phase (30,000 to 500,000 m³/day) with maintained reliability
Reinforced project positioning as global benchmark for sustainable infrastructure development through optimized, resilient design
Delivered actionable insights supporting both engineering design finalization and lifecycle cost optimization strategies